√画像をダウンロード greenhouse gas effect graph 687609-What is greenhouse gas and its effect
Methane (CH 4), which causes 4–9 percent;Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived keeling curve graphic CO2 traps twothirds of the heat retained on the Earth's surface by greenhouse gases, and this warming effect has increased by 45% since 1990

Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
What is greenhouse gas and its effect
What is greenhouse gas and its effect- The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric CO 2This chart maps out future greenhouse gas emissions scenarios under a range of assumptions if no climate policies were implemented;




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Animal Agriculture Greenhouse gases (GHGs) absorb infrared radiation and cause the greenhouse effect, which warms the Earth1 GHGs are both natural gases, such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and nitrous oxide, as well as humanmade gases, including chloro and hydrofluorocarbons2 The graphic paints a picture of how that looks for each country China's emissions for energy alone make up nearly percent of total global Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They let
Synonyms for greenhouse gas in Free Thesaurus Antonyms for greenhouse gas 1 synonym for greenhouse gas greenhouse emission What are synonyms for greenhouse gas?Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases, and the primary greenhouse gases on Earth are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Of these, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), have an appreciable greenhouse effect, and are being released in large quantities by human activityThe gases that trap heat in Earth's atmosphere, Earth would be a frigid desert like Mars (average temperature 55°C, or 67°F) Too much greenhouse gas and Earth could be a fiery inferno like Venus (average temperature 450°C, or 850°F) On the Greenhouse Effect Gizmo, set the Greenhouse gases to 0% and the Simulation speed to fast 1
The other greenhouse gas emissions would also limit the warming effect resulting from declining aerosol pollution and would improve air"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, but the extra gases produced by human activity are making it stronger We are now adding to these gases faster than oceans and plants can absorb them — the greenhouse effect is being 'enhanced' by humans



Graph Of The Day Antropocene Atmospheric Experiment Ghg Climate Forcing Increased 29 Over Years Bits Of Science




This Graph Shows The Increase In Greenhouse Gas Ghg Concentrations In Download Scientific Diagram
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)Carbon dioxide (CO 2), which causes 9–26 percent;The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide is roughly the same no matter
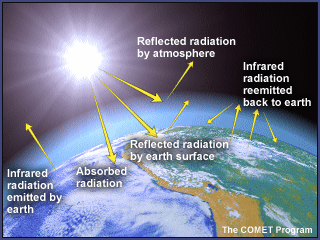



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
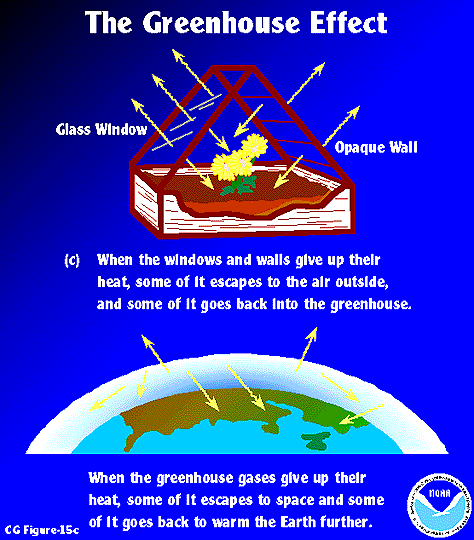



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
Let's have a look at the greenhouse effect (see also the graph about radion transmitted by atmosphere below) About 70 to 75% of the solar radiation passes through the atmosphere and reaches the Earth This solar radiation is absorbed on the Earth surface, which warms up the Earth surface When a body is warmer than its environment, it emitsThe greenhouse effect has supported life on the earth for millions of years Today, however, the greenhouse effect is growing stronger as human activities such as deforestation and fossil fuel use release more and more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere This traps greater amounts of the sun's radiation, which contributes to rising temperatures, also known as global warmingLargely caused by the humaninduced increase of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere The data in this graph show that temperatures have risen and fallen with CO2 concentrations over the last 400,000 years More recent data have shown the same relationship extends 650, 000 years or more Gas



3




What Best Explains The Graph Shown Below A Temperature Is Dropping Because Greenhouse Gases Are Brainly Com
The report puts a spotlight on 4 sectors that are the biggest contributors of greenhouse gas emissions energy, industrial processes, agriculture, and waste generation The use of coal and fuel oil for electricity generation contributed 418 percent, almost half of the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the country in 10 and is growing annually by 37 percentOn Earth, the major greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 36–70 percent of the greenhouse effect (not including clouds); Nowadays we hear a lot about the "greenhouse effect" because the Earth is warm and it is some gases in the air (greenhouse gases) that are responsible for keeping the Earth warm and suitable for life as we know it Energy from sunlight is the source of the warmth in a greenhouse, because the sunlight can pass right through the transparent



1



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an important heattrapping (greenhouse) gas, which is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, as well as natural processes such as respiration and volcanic eruptions The first graph shows atmospheric CO 2 levels measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, in recent years, with The graph below is based upon absorption data for water vapor and carbon dioxide given in JR Houghton's The Physics of Atmospheres The effects of the greenhouse gases are the same on clear and cloudy nights so the difference comes entirely from the difference inAnd ozone, which causes 3–7 percentThe issue is how the strength of the greenhouse effect changes when human activity increases the atmospheric




File Limiting Global Warming To 2 Degrees Celsius Options To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pbl Png Wikimedia Commons




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
This graph shows the heating imbalance caused by the major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide (gray), methane (dark purple), nitrous oxide (medium purple), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs, lavender), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs, blue), and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs, light blue) Just another day at the office Climate365 graphic Graphic Another day at the office Carbon dioxide is the main heattrapping greenhouse gas that humans emitGreenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gasThe largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and Russia



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
And necessary pathways which are compatible with limiting warming to 15°C or 2°C of warming this century 14 Greenhouse gas emissions by sector in the EU According to the fifth assessment report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is extremely likely that human activities over the past 50 years have warmed our planet These activities include for example the burning of coal, oil and gas, deforestation and farming Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere, the Earth would be much colder on average than it is now Greenhouse gases absorb energy




Graphic The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
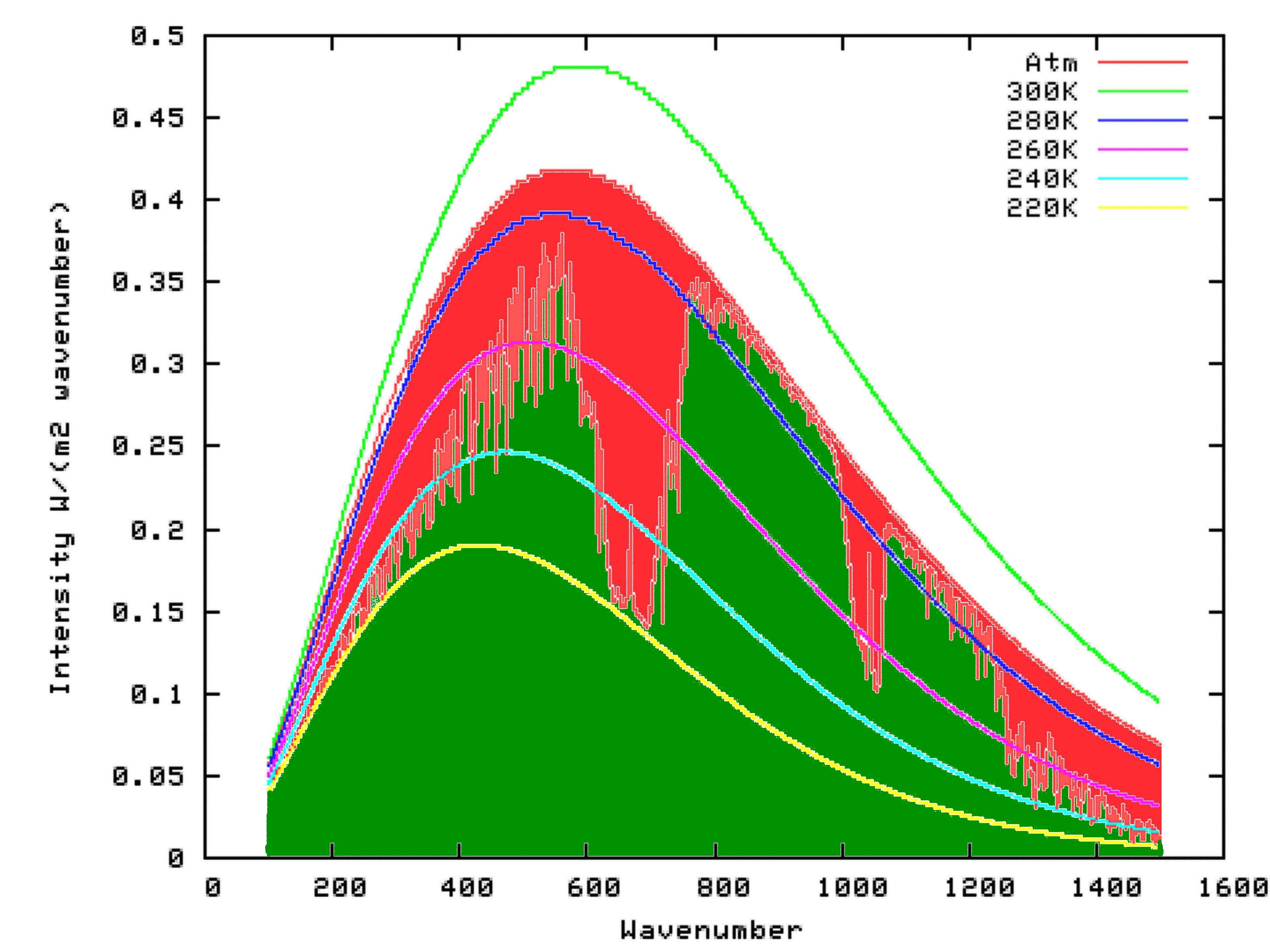



Greenhouse Effect Basics Warm Earth Cold Atmosphere
The enhanced greenhouse effect What has scientists concerned now is that over the past 250 years, humans have been artificially raising the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at an everincreasing rate, mostly by burning fossil fuels, but also from cutting down carbonabsorbing forests Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclearIf current policies continued;



Global Warming A Closer Look At The Numbers
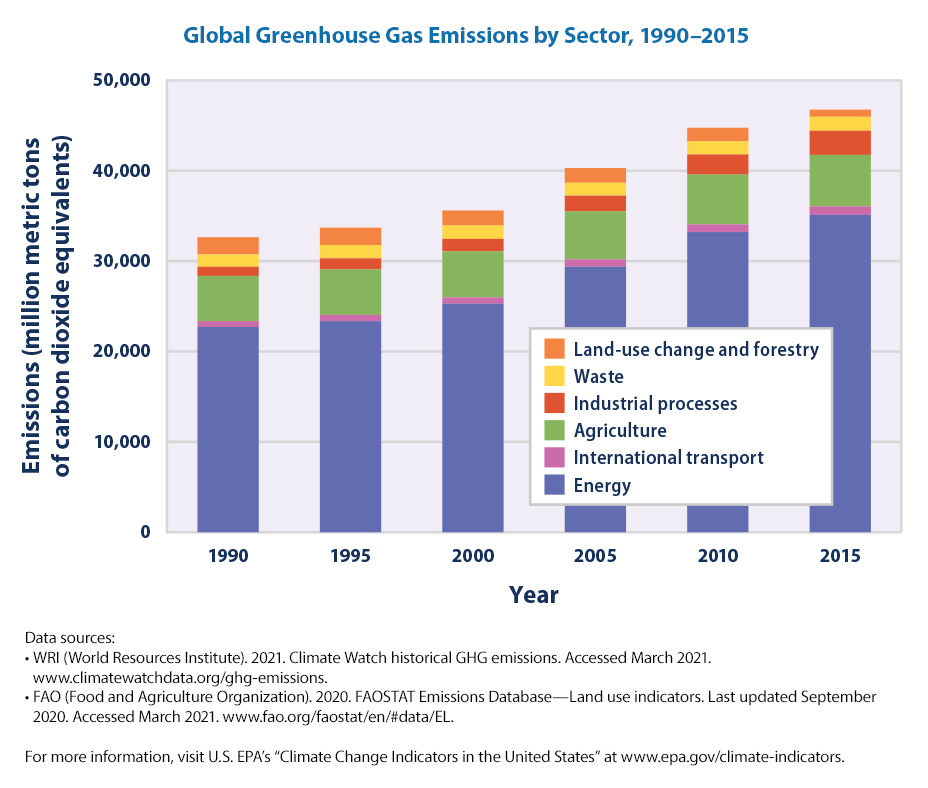



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
Larger image to save or print Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases This section provides information on emissions and removals of the main greenhouse gases to and from the atmosphere For more information on the other climate forcers, such as black carbon, please visit the Climate Change Indicators Climate Forcing pageSynonyms for Greenhouse gases in Free Thesaurus Antonyms for Greenhouse gases 1 synonym for greenhouse gas greenhouse emission What are synonyms for Greenhouse gases?NASA satellites record a host of vital signs including atmospheric aerosols (particles from both natural sources and human activities, such as factories, fires, deserts, and erupting volcanoes), atmospheric gases (including greenhouse gases), energy radiated from Earth's surface and the Sun, ocean surface temperature changes, global sea level, the extent of ice sheets, glaciers and



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
New Zealand greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions have been relatively unchanged since 05 In 18 New Zealand's gross greenhouse gas emissions were 7 million tonnes of CO 2e, 240 percent higher than 1990 and 10 percent lower than 17 In 18Energy use and greenhouse gas emissions A wide variety of factors have an influence on the level of GHG emissions in Canada Globally, about 78% of GHG emissions from human activity are from the production and consumption of energyThe greenhouse effect is the warming of Earth due to carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere Warming occurs as sunlight strikes the Earth Much of the sunlight is reflected back into space But Earth's atmosphere absorbs much of the heat and slows its escape from Earth In this way, the Earth is like a greenhouse




Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education
If all countries achieved their current future pledges for emissions reductions; Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 14, CO 2 accounted for about 809% of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)Greenhouse gases play a major role in regulating Earth's climate Without the gases that trap heat in Earth's atmosphere, Earth would be a frigid desert like Mars (average temperature 55°C, or 67°F) Too much greenhouse gas and Earth could be a fiery inferno like Venus (average temperature 450°C, or 850°F) On the Greenhouse Effect




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
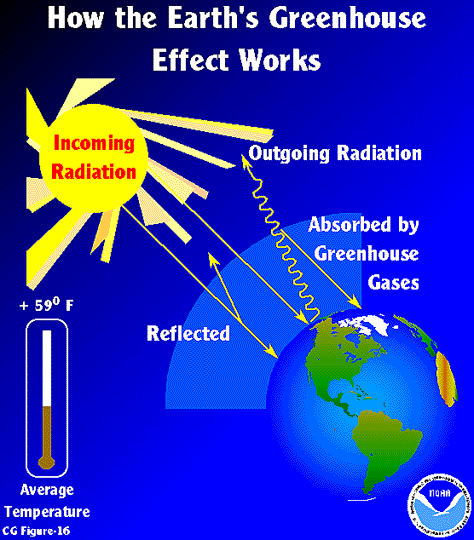



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
Greenhouse gas emissions from electricity have increased by about 12 percent since 1990 as electricity demand has grown and fossil fuels have remained the dominant source for generation To learn about projected greenhouse gas emissions to , visit the US Climate Action Report 14 (310 pp, 23 M, About PDF)This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnes




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic By Mind The Graph The Science Educator Medium



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
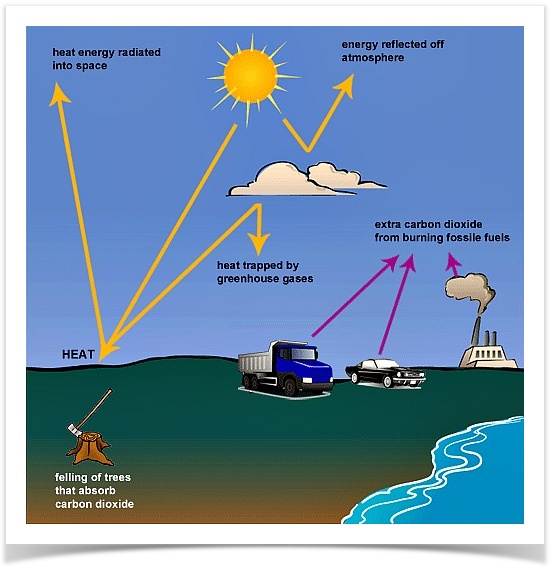



Graph Writing 162 Greenhouse Gases Trap Energy From The Sun




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




1zrlfbmrqd Vwm
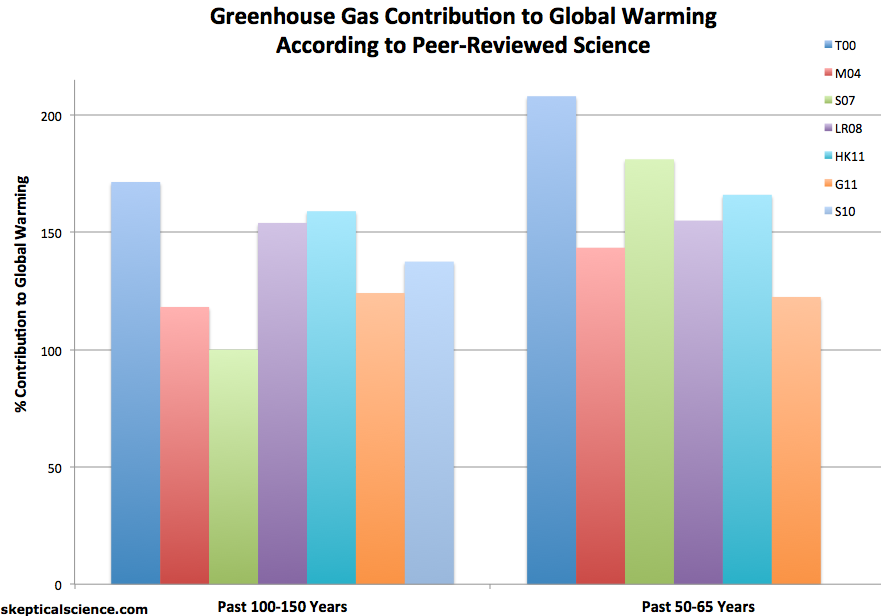



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming




What S Going On In This Graph Nov 19 The New York Times



The Greenhouse Effect
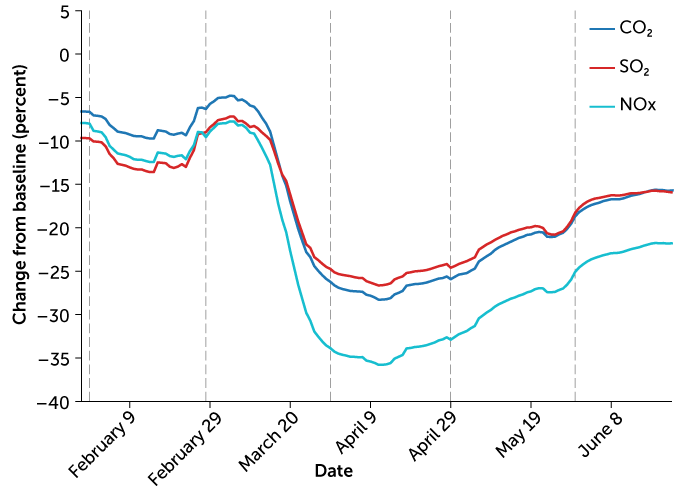



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News



Greenhouse Conservation Biodiversity Sustainability Environment Issues Automated Lobbying Database At Information For Action
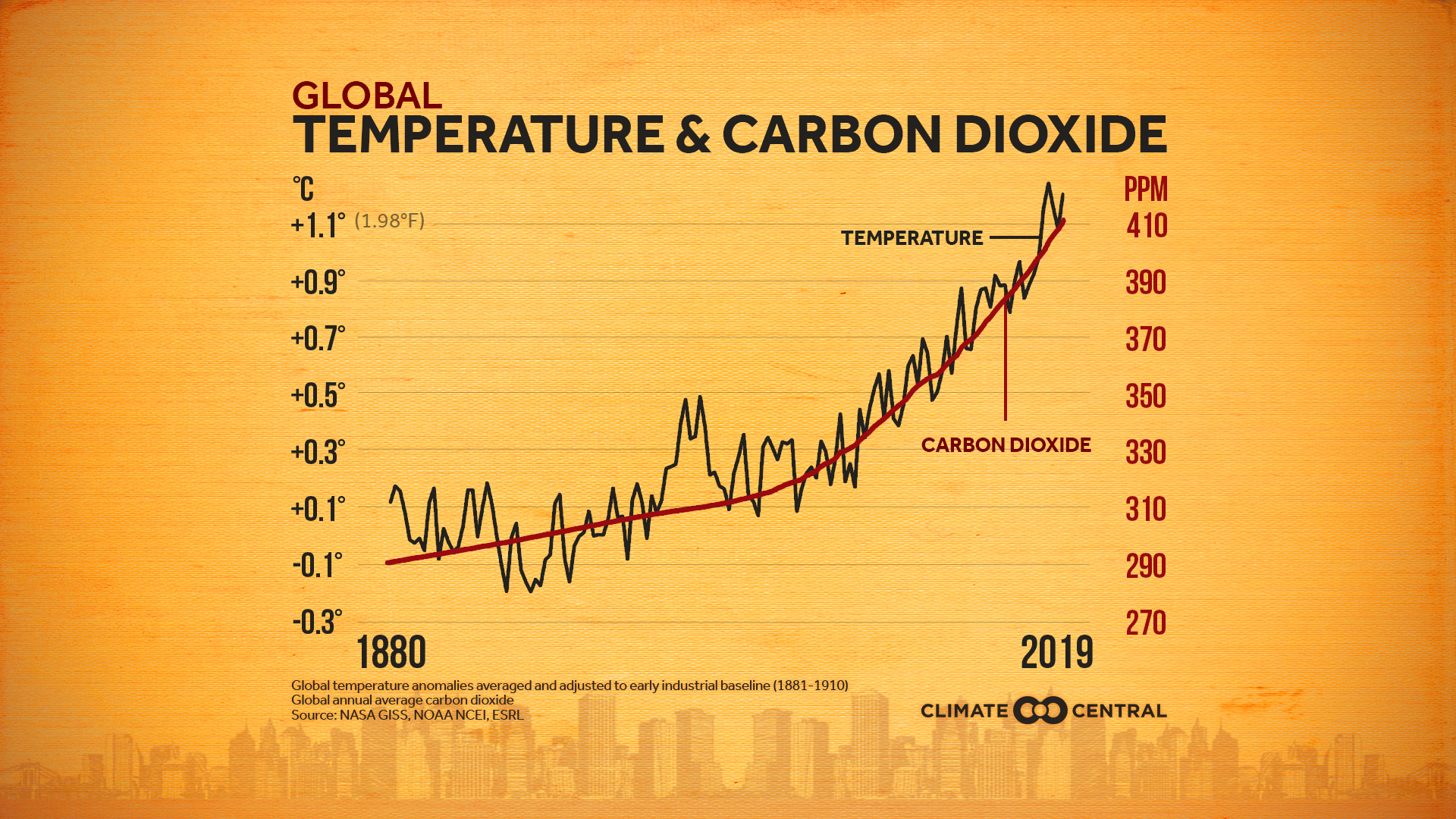



Emissions Sources Climate Central
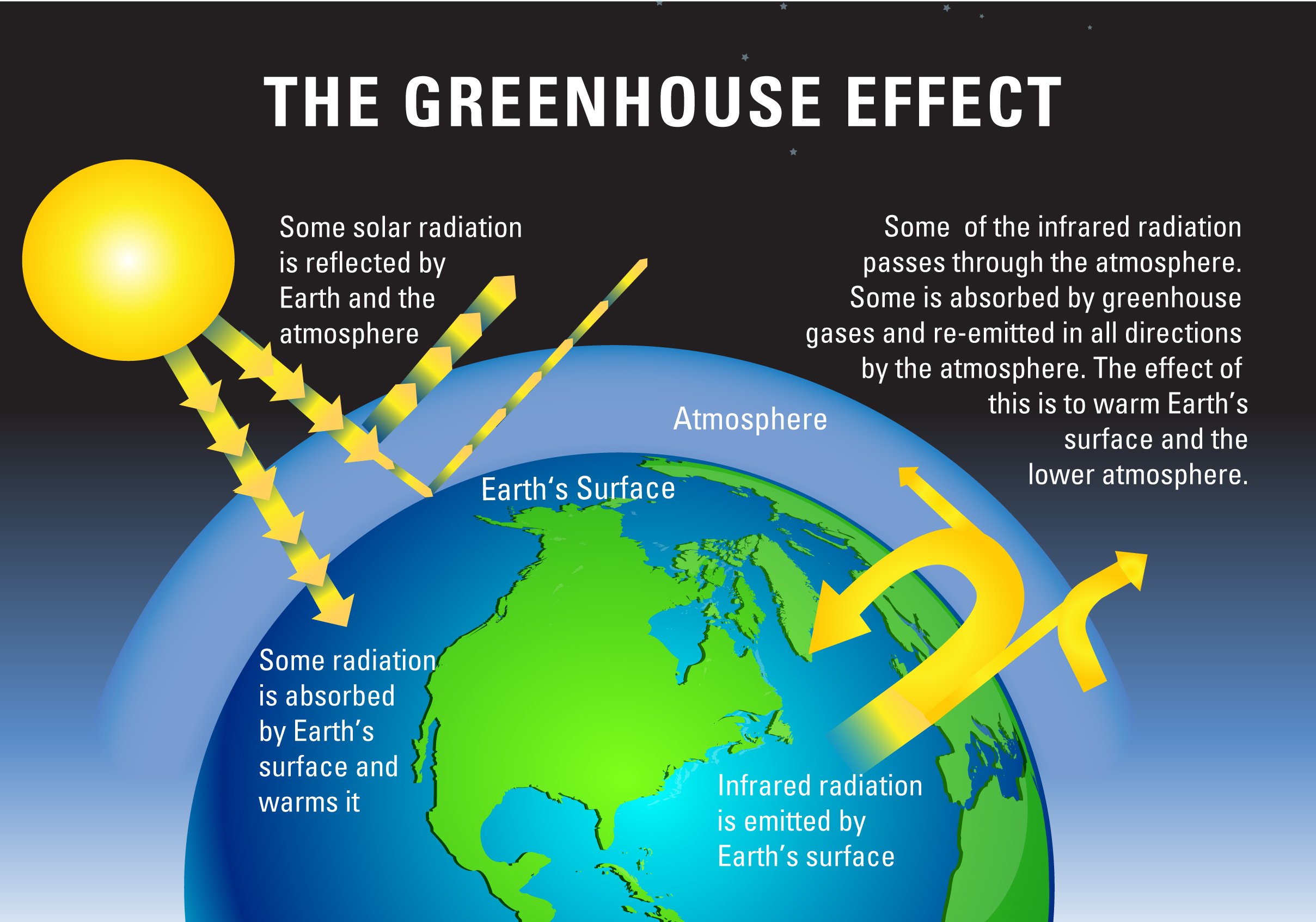



Greenhouse Gases Earth Journalism Network



3




Indicator Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Indicator Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Gcis
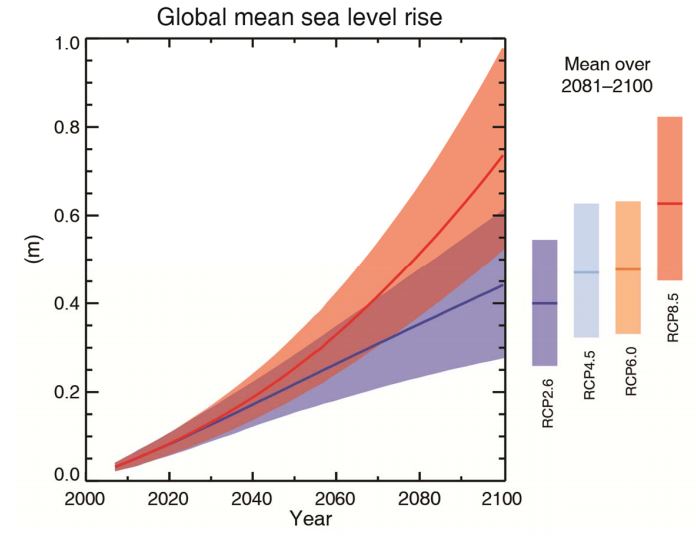



Ipcc Six Graphs That Explain How The Climate Is Changing Carbon Brief



Manhassetschools Org




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
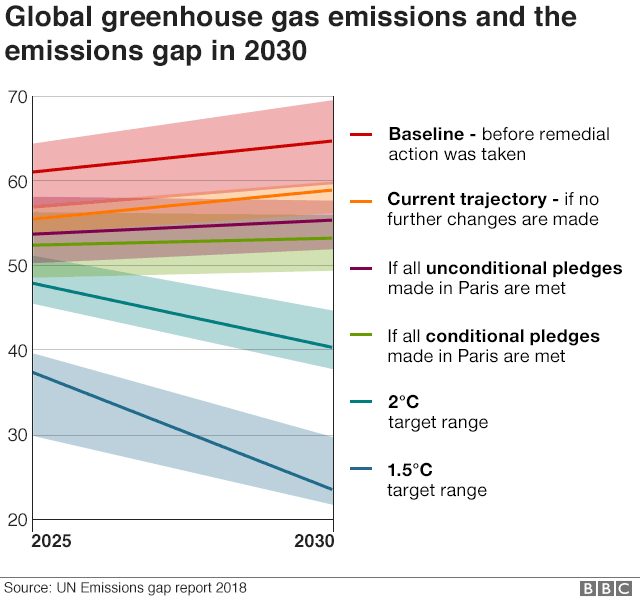



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Are Humans Causing Or Contributing To Global Warming Noaa Climate Gov



Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
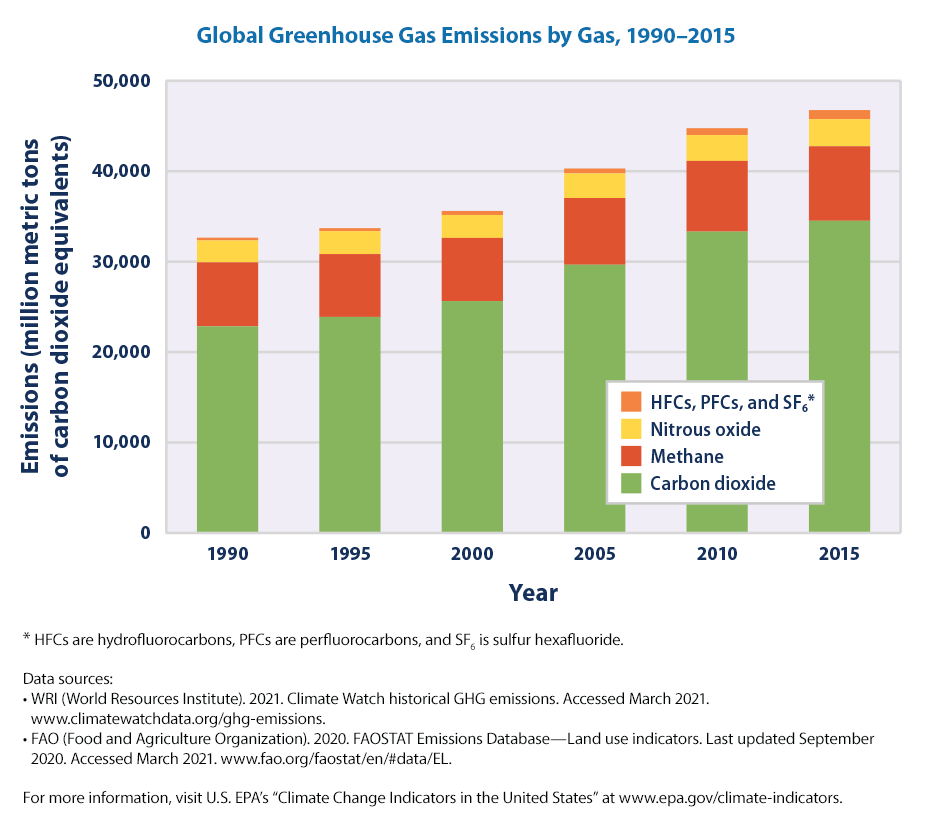



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
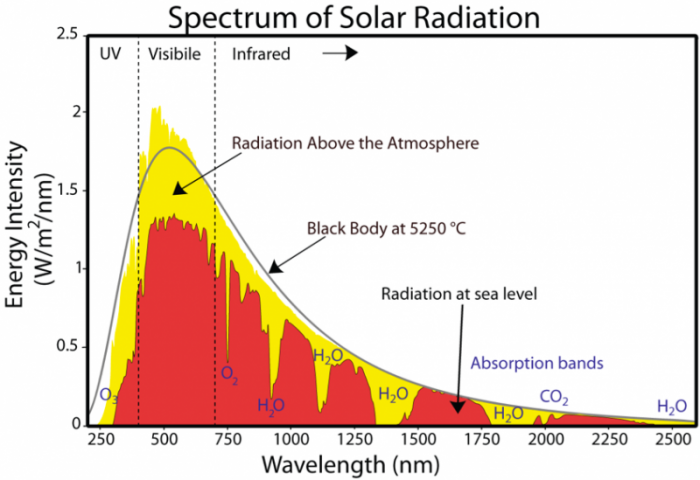



The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Energy Budget Earth 103 Earth In The Future



The Greenhouse Effect




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
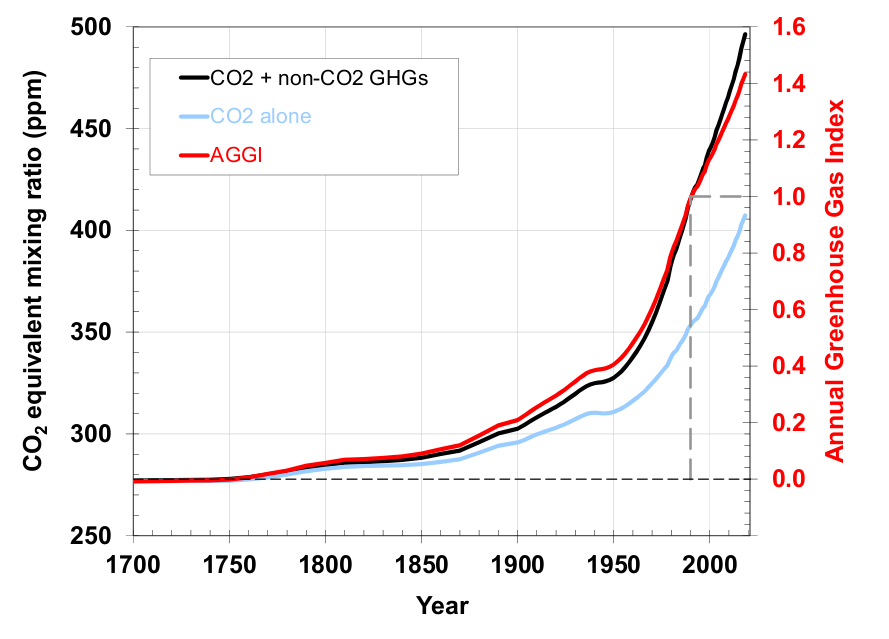



Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index 1700 18 Desdemona Despair




Lower Emissions Cap For Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative Takes Effect In 14 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Notice That A Sudden Change Occurred At The Start Of Day 4 In The Graph Below What Change In Brainly Com
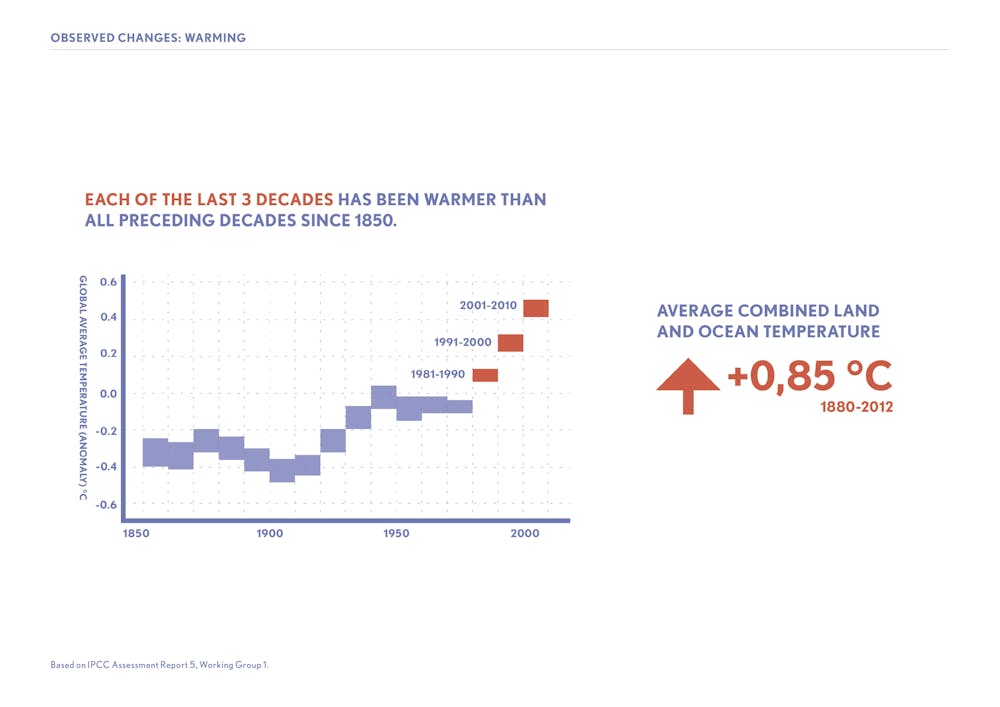



What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
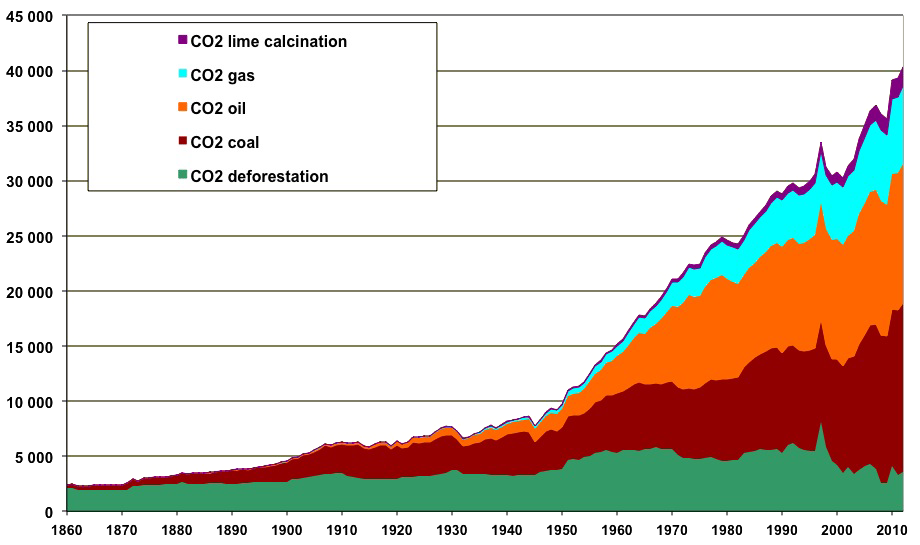



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici



The Greenhouse Effect Pveducation




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



1
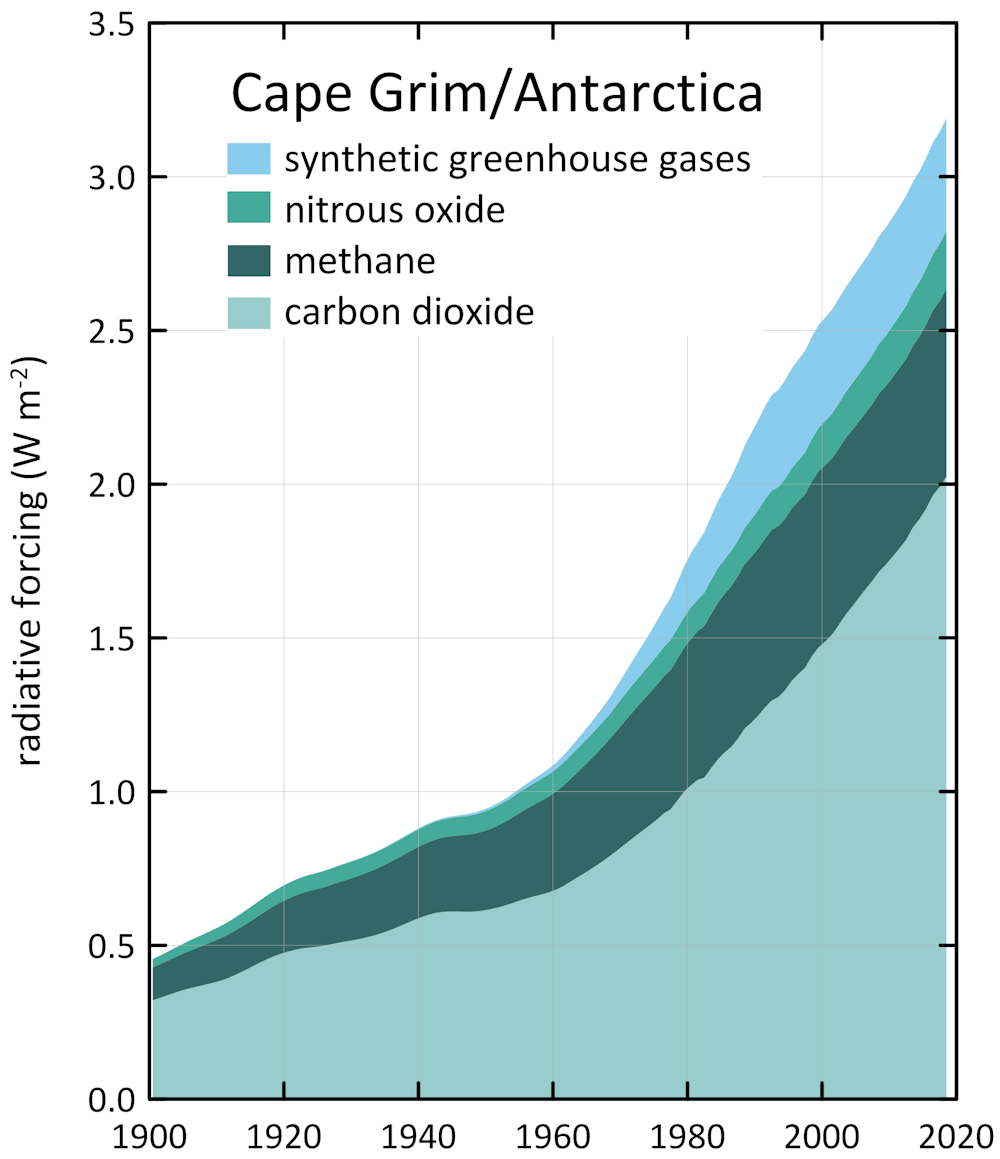



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised




Washington S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Continue To Trend Higher In Latest Inventory The Seattle Times



c News World Greenhouse Gas Emissions Rising



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Effects Greenhouse Effect
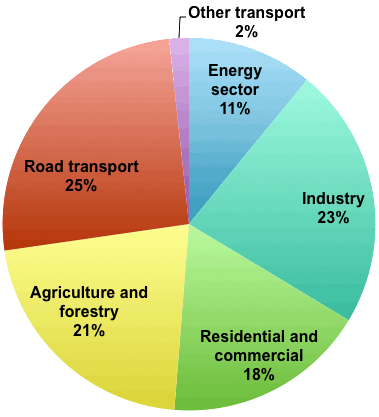



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
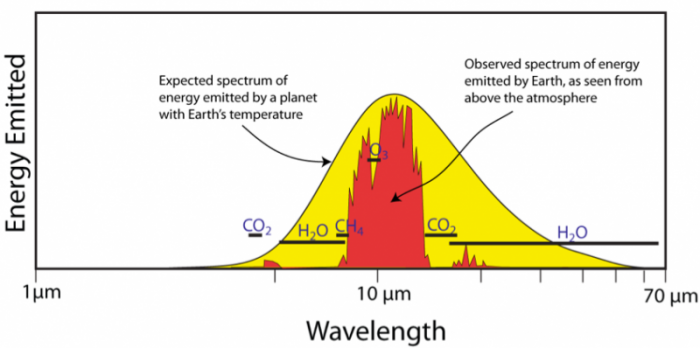



The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Energy Budget Earth 103 Earth In The Future
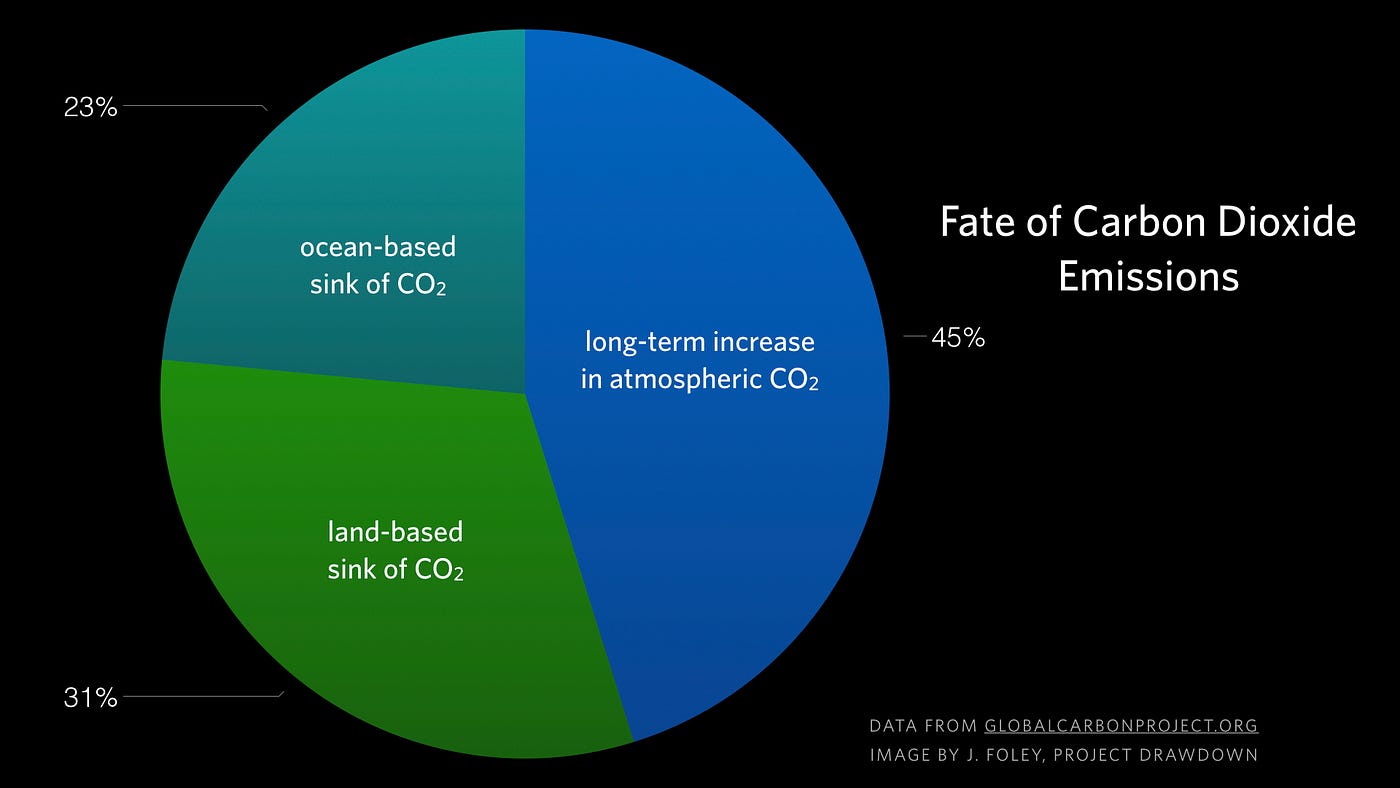



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org
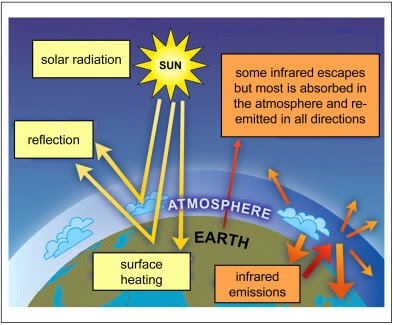



Part 1 Back To The Start How Did We Get Into This Climate Mess And Is It Really That Bad Extinction Rebellion Uk
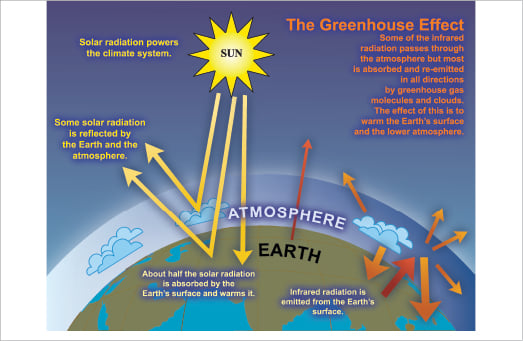



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science
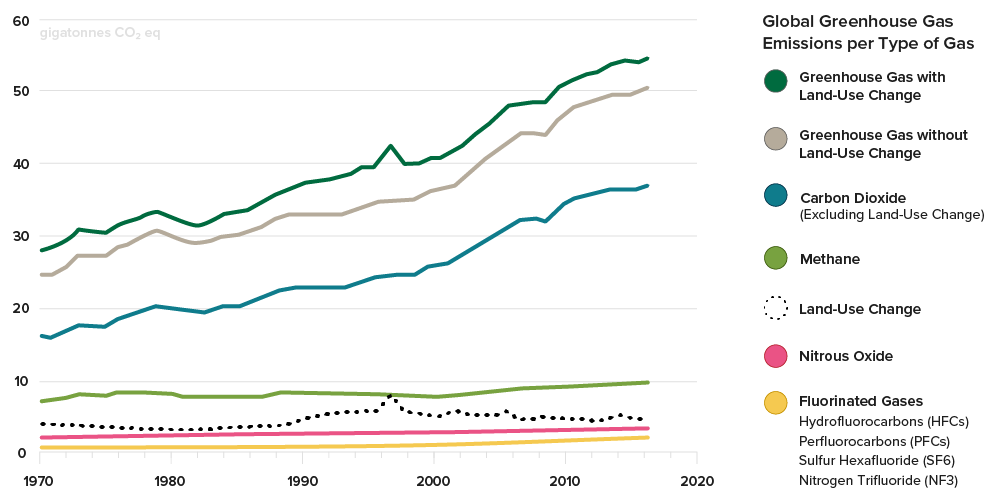



Carbon Emissions Forestry Carbon Credits The Arbor Day Foundation




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Kidminds




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
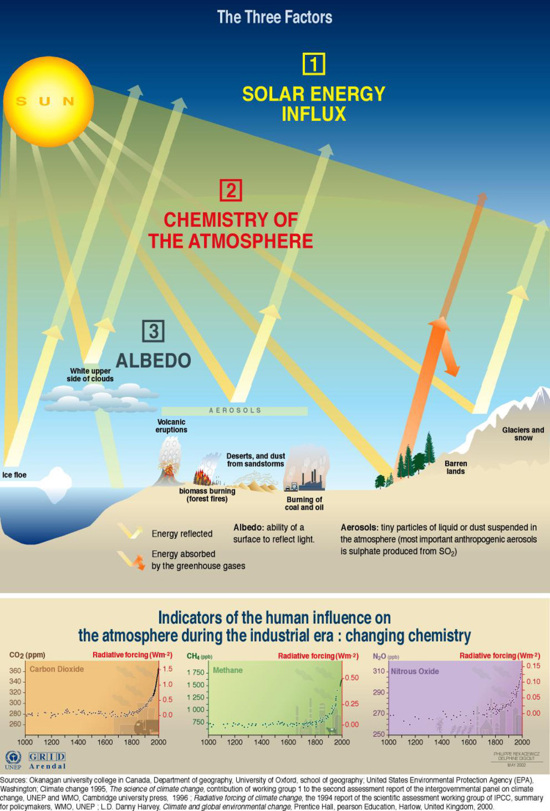



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal




California Plans To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions 40 By 30 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia
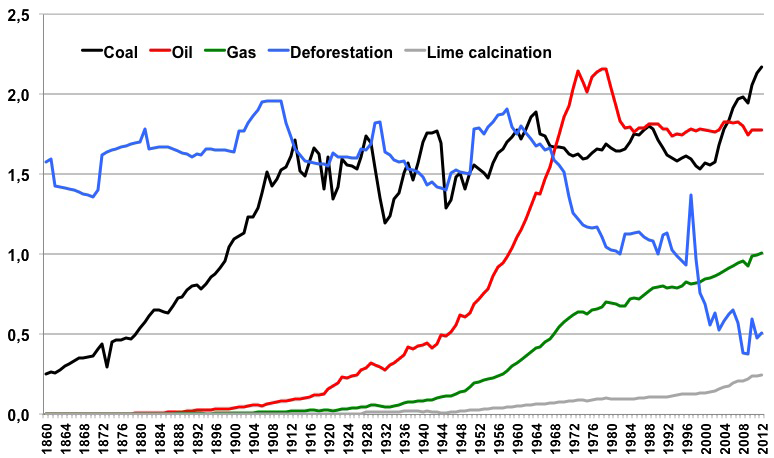



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici




California Plans To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions 40 By 30 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia
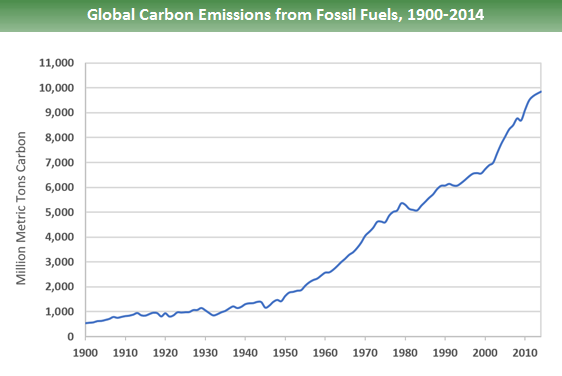



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming



Greenhouse Gas Emissions By The United States Wikipedia
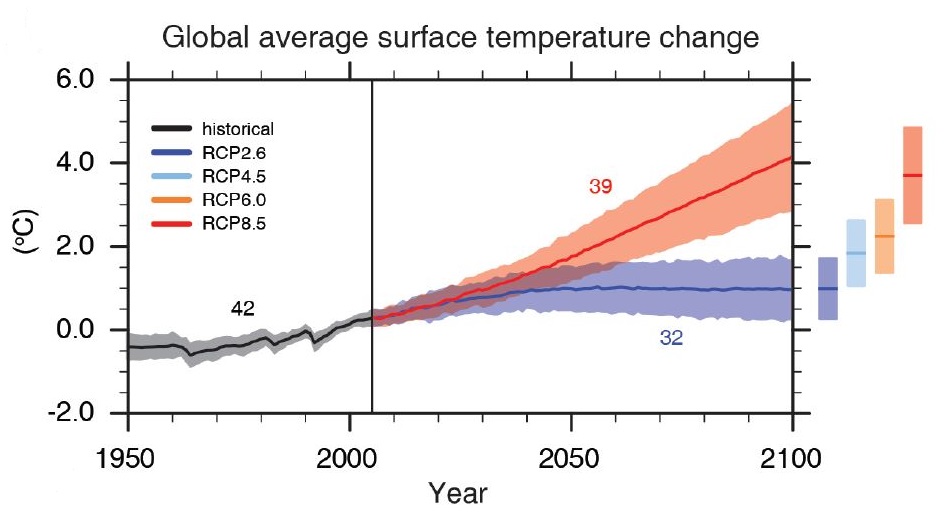



Ipcc Six Graphs That Explain How The Climate Is Changing Carbon Brief




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research
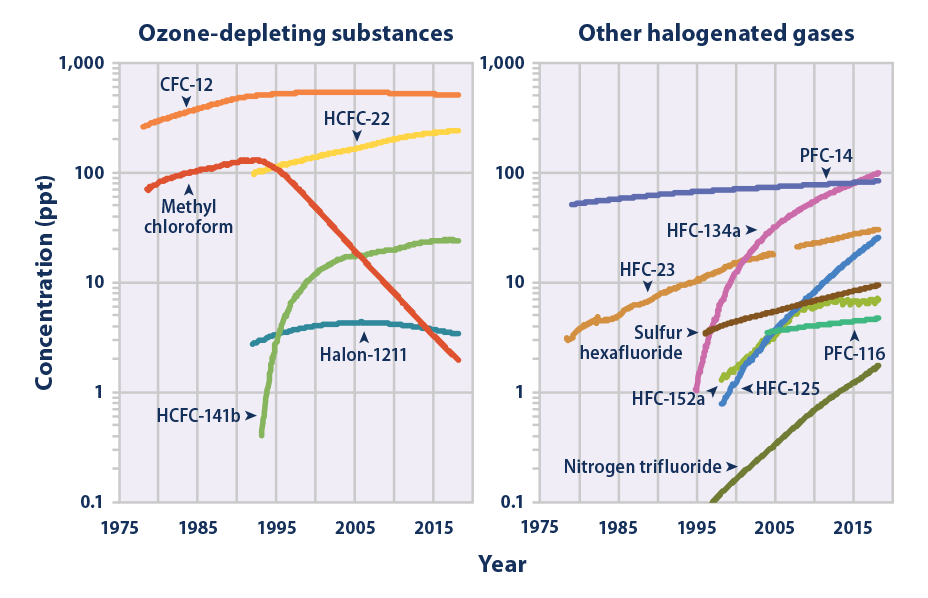



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
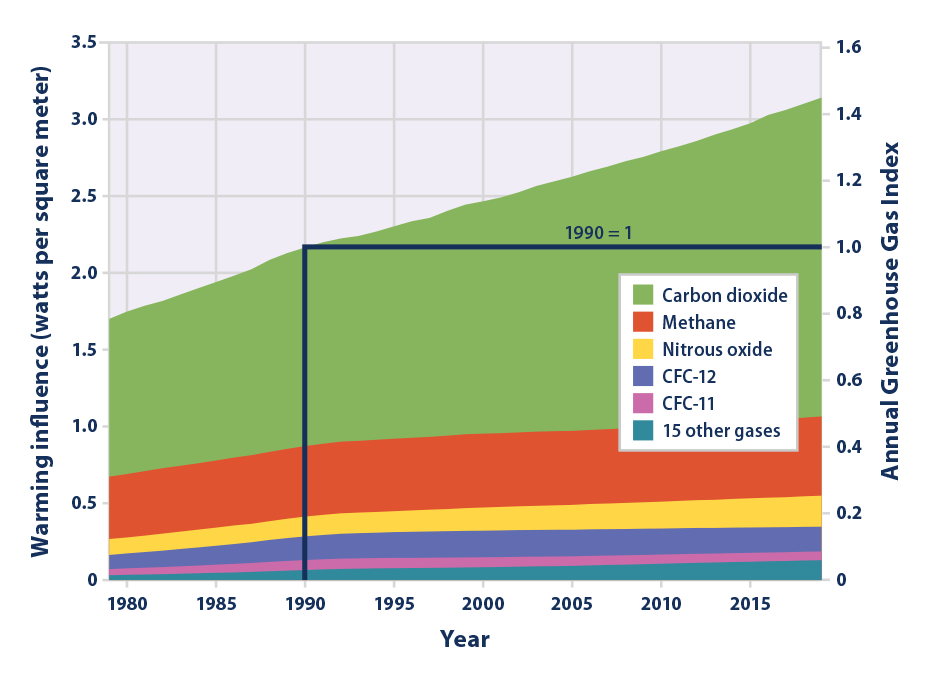



Climate Change Indicators Climate Forcing Us Epa




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
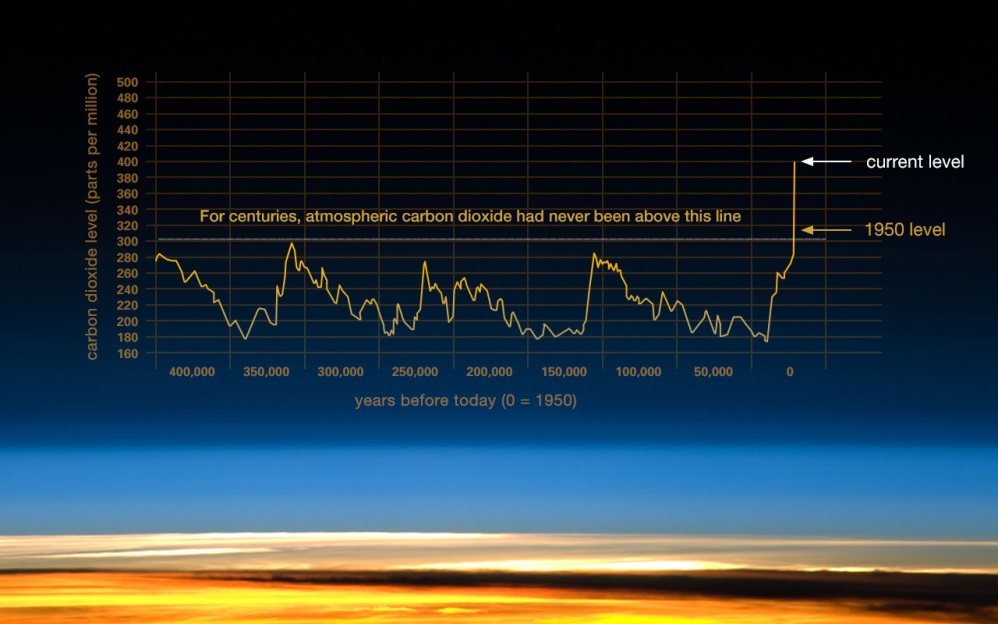



Causes And Greenhouse Effect
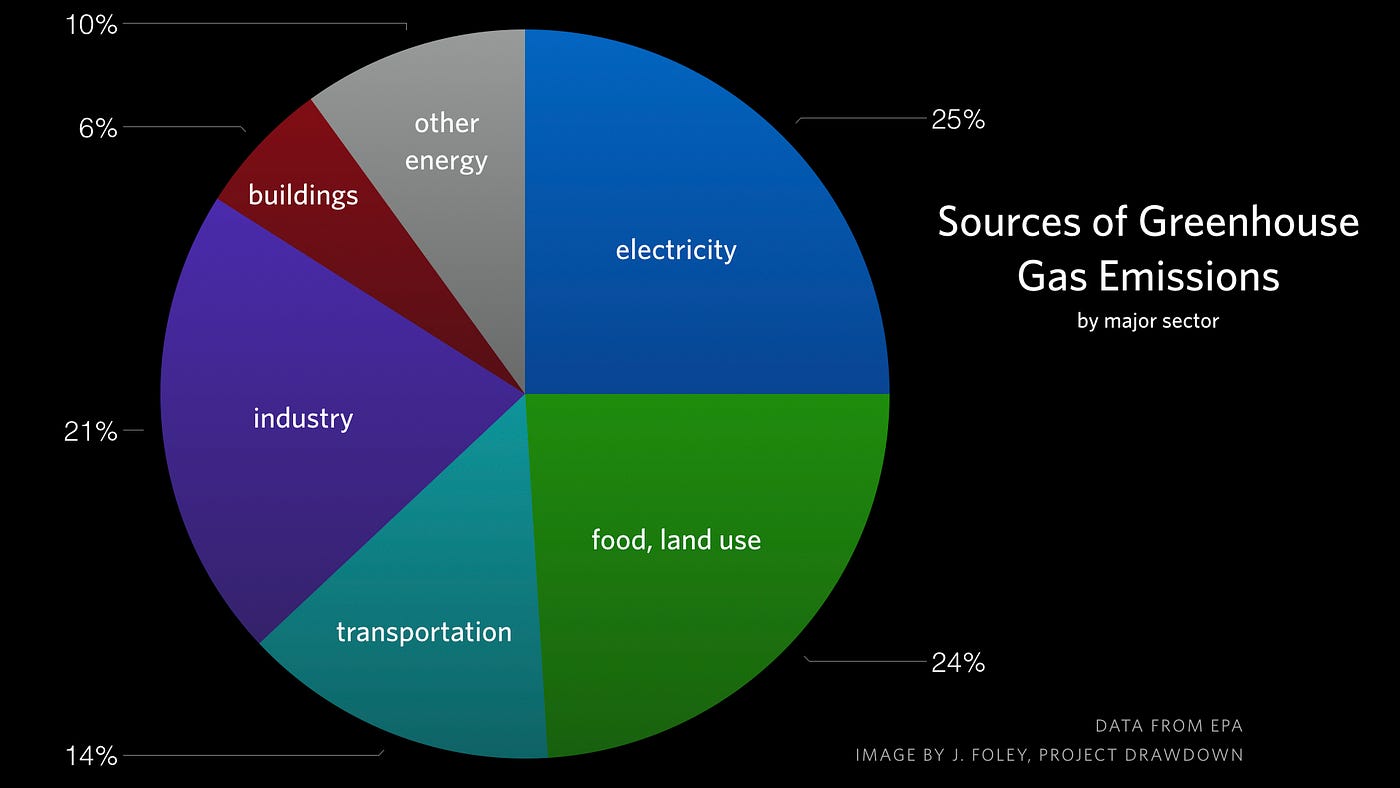



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Were Stopped Would The Climate Return To The Conditions Of 0 Years Ago Royal Society
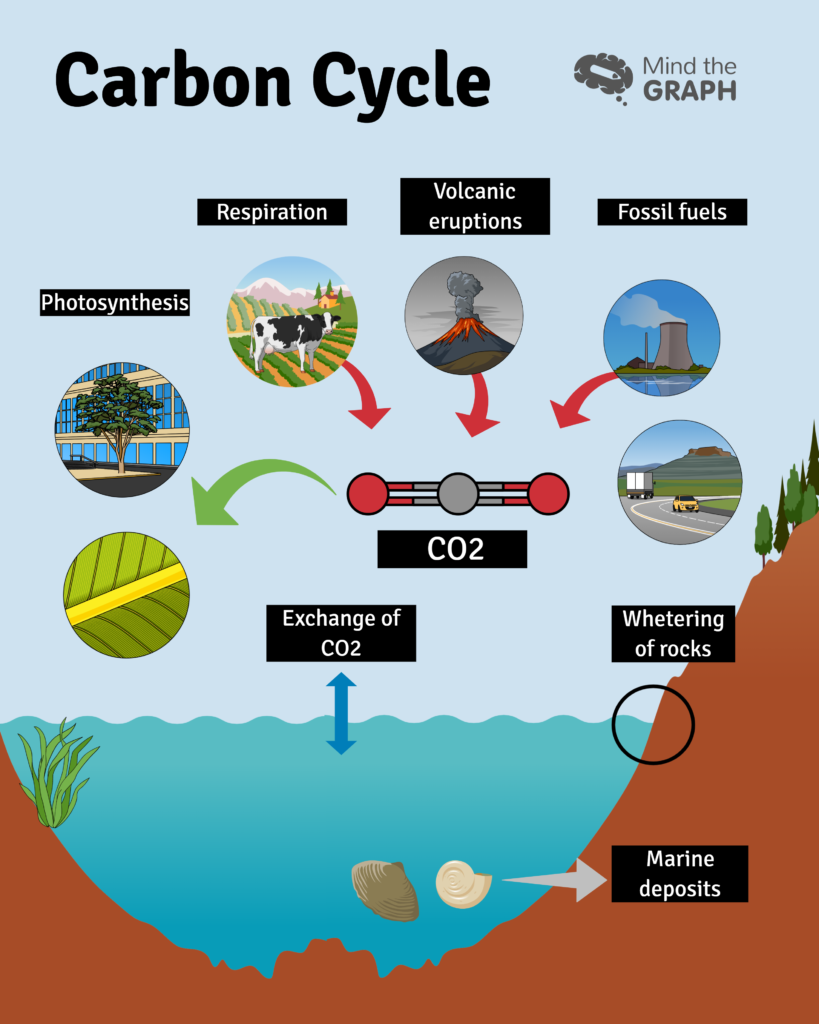



Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic By Mind The Graph The Science Educator Medium
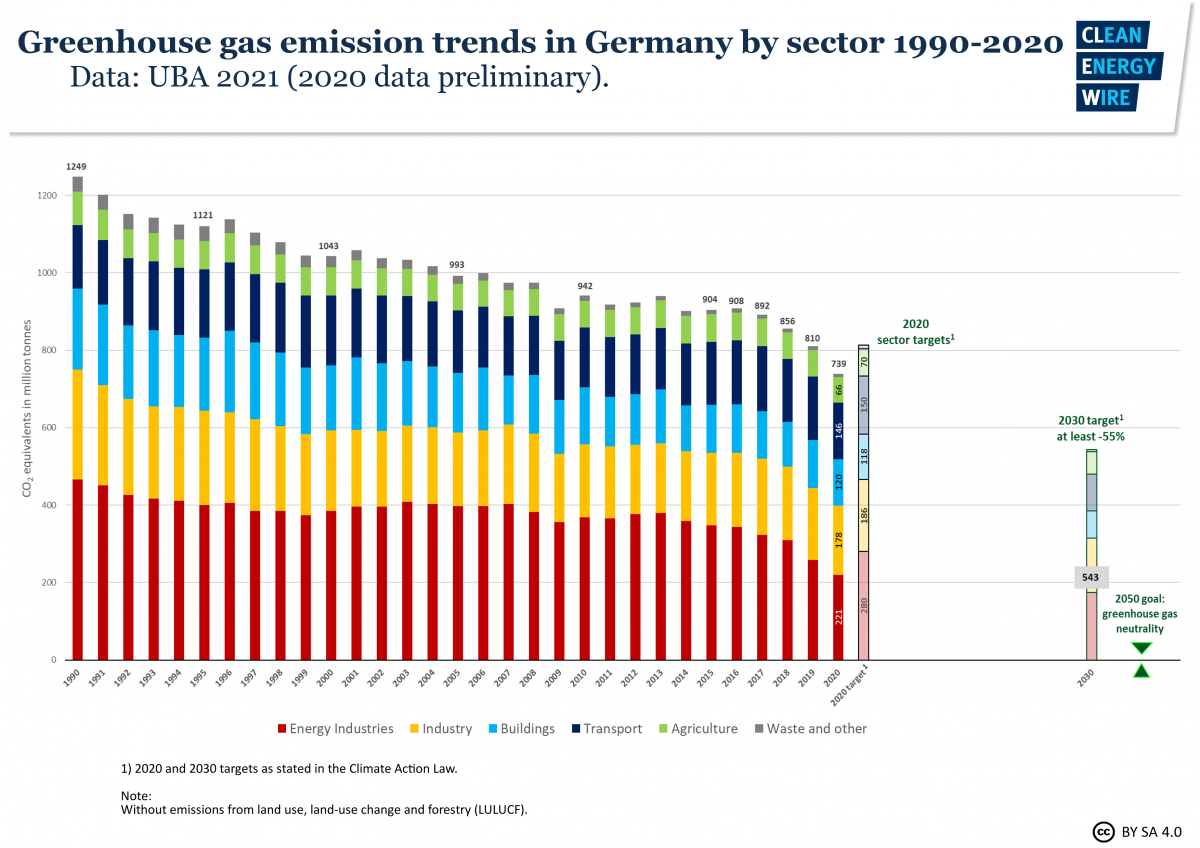



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire
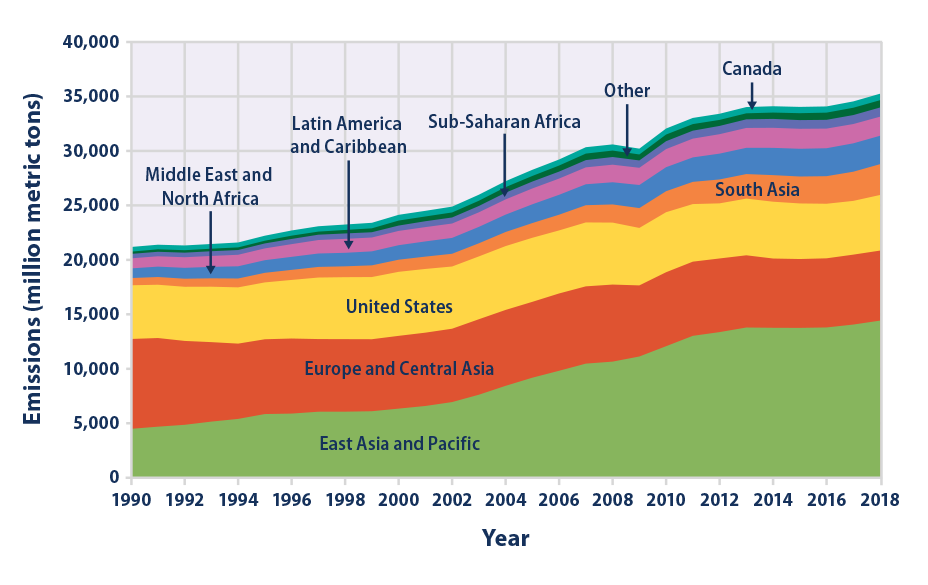



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




What Are Greenhouse Gases Domesticgoddessguidetocc
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
コメント
コメントを投稿